What Is Mobile Payment And How Does It Work
adminse
Apr 06, 2025 · 8 min read
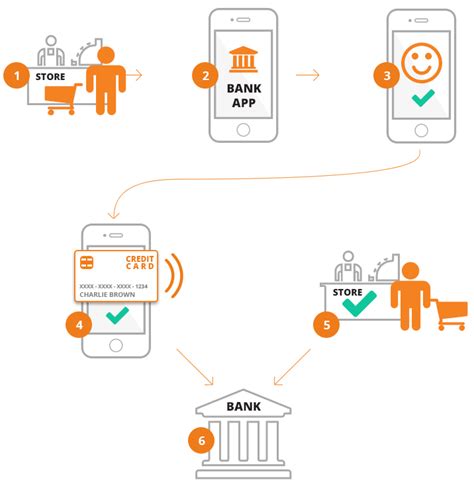
Table of Contents
Decoding Mobile Payments: A Comprehensive Guide to How It Works
What if the future of commerce resides in the palm of your hand? Mobile payment systems are rapidly transforming how we transact, offering unparalleled convenience and efficiency.
Editor’s Note: This article on mobile payments was published today, providing readers with the latest insights and understanding of this rapidly evolving technology.
Why Mobile Payments Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Mobile payments are no longer a futuristic concept; they are a ubiquitous reality reshaping global commerce. From everyday purchases to large-scale transactions, the ability to pay using a smartphone has revolutionized how businesses operate and consumers spend. This technology offers enhanced convenience, speed, and security compared to traditional methods. The implications are far-reaching, impacting businesses of all sizes, fostering financial inclusion, and driving innovation in the fintech sector. Its impact on various industries, from retail and hospitality to transportation and healthcare, cannot be overstated. Understanding the intricacies of mobile payments is crucial for anyone navigating the modern economic landscape.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This comprehensive guide delves into the core mechanics of mobile payment systems. We will explore different types of mobile payments, examining their underlying technologies, security measures, and the benefits they offer to both consumers and businesses. We will also analyze the global landscape of mobile payments, highlighting key players and future trends. Finally, we'll discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with this rapidly growing sector.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon reputable sources including industry reports from firms like Gartner and Forrester, academic publications, and news articles from trusted media outlets. The information presented is based on a thorough review of existing literature and a comprehensive analysis of the mobile payment ecosystem.
Key Takeaways: Summarize the Most Essential Insights
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear explanation of mobile payments, encompassing various types and technologies.
- Types of Mobile Payments: A detailed breakdown of different mobile payment methods, including NFC, QR codes, and mobile wallets.
- How Mobile Payments Work: A step-by-step guide explaining the transaction process from initiation to completion.
- Security Measures: An overview of the security protocols implemented to protect user data and prevent fraud.
- Benefits and Challenges: A balanced assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of mobile payments.
- Future Trends: An exploration of the emerging technologies and trends shaping the future of mobile payments.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance and scope of mobile payments, let's now delve into the specifics of how these systems function, examining their various forms and the technology that underpins them.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Mobile Payments
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Mobile payment, or mobile money, refers to the use of mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets to make payments for goods and services. It eliminates the need for physical cash or cards, streamlining transactions and offering increased convenience. This encompasses a broad range of technologies and services, all focused on enabling electronic transactions via a mobile interface.
2. Types of Mobile Payments:
Several key methods underpin mobile payment systems:
-
Near Field Communication (NFC): This technology allows for contactless payments by bringing a mobile device within close proximity to a payment terminal. Examples include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay. NFC uses radio waves to transmit data securely over short distances.
-
QR Code Payments: These payments involve scanning a QR code displayed by a merchant using a mobile device’s camera. The payment information is then processed through a connected mobile wallet or payment app. This is particularly popular in regions like Asia.
-
Mobile Wallets: These are digital wallets stored on mobile devices, allowing users to store payment information, loyalty cards, and other digital assets. Examples include Apple Wallet, Google Wallet, and PayPal. These wallets often integrate with various payment methods, providing a centralized platform for managing transactions.
-
SMS-Based Payments: Some mobile payment systems utilize SMS (text messaging) to initiate and complete transactions. This is particularly useful in regions with limited internet access.
-
In-App Payments: Many mobile apps allow users to make payments directly within the application, often linked to their mobile wallet or credit/debit card.
3. How Mobile Payments Work (A Step-by-Step Guide):
Let's illustrate the process using NFC as an example:
-
User Initiates Payment: The user selects the mobile payment app and holds their NFC-enabled device near the payment terminal.
-
Device Communication: The device communicates with the payment terminal via NFC, transmitting payment information securely.
-
Authentication: The payment is authenticated using biometric methods (fingerprint, facial recognition) or a PIN.
-
Transaction Processing: The payment processor verifies the transaction with the user's bank or payment provider.
-
Confirmation: The user receives a confirmation message on their device, indicating successful completion of the transaction.
4. Security Measures:
Security is paramount in mobile payment systems. Several measures are employed to mitigate risks:
-
Tokenization: Replacing sensitive payment card details with unique tokens, reducing the risk of data breaches.
-
Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data during transmission and storage to protect against unauthorized access.
-
Biometric Authentication: Using fingerprint or facial recognition to verify user identity.
-
Two-Factor Authentication: Requiring an additional verification step beyond the password, enhancing security.
-
Fraud Monitoring: Constant monitoring for suspicious activities to prevent and detect fraudulent transactions.
5. Benefits and Challenges:
Benefits:
- Convenience: Eliminates the need for physical cash or cards, streamlining transactions.
- Speed: Transactions are processed quickly, reducing waiting times.
- Security: Advanced security measures help to protect user data and prevent fraud.
- Tracking and Management: Easy tracking of transactions and managing finances through mobile apps.
- Financial Inclusion: Providing access to financial services for the unbanked population.
Challenges:
- Security Concerns: While security measures are robust, the potential for fraud remains a concern.
- Technical Issues: Reliance on technology means transactions can be disrupted by connectivity issues.
- Consumer Adoption: Not all consumers are comfortable using mobile payments.
- Merchant Adoption: All merchants need to be equipped with the necessary infrastructure to accept mobile payments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating diverse regulatory requirements across different countries can be complex.
6. Future Trends:
The future of mobile payments is dynamic, with several key trends emerging:
- Increased Integration: Further integration with other services, like loyalty programs and rewards systems.
- Biometric Authentication Advancements: More sophisticated and secure biometric technologies.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Integration: The potential for incorporating blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies into mobile payment systems.
- AI-Powered Personalization: Utilizing AI to personalize payment experiences and offer tailored services.
- Growth in Emerging Markets: Significant growth in mobile payments adoption is expected in developing countries.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Mobile payments represent a fundamental shift in how commerce is conducted. Their convenience, speed, and enhanced security are driving widespread adoption across the globe. While challenges remain, the continued development of innovative technologies and robust security protocols is solidifying mobile payments’ place as a dominant force in the global financial landscape.
Exploring the Connection Between Security Concerns and Mobile Payments
Security is intrinsically linked to the widespread adoption and success of mobile payment systems. Any perceived weakness in security can deter consumers from utilizing this technology.
Key Factors to Consider:
Roles and Real-World Examples: Security breaches in major mobile payment systems have highlighted the importance of robust security measures. For example, incidents of data breaches in the past have emphasized the need for advanced encryption and tokenization techniques.
Risks and Mitigations: The risks associated with mobile payments include data breaches, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access. Mitigations include implementing strong authentication methods like two-factor authentication, employing advanced encryption techniques, and regularly updating software.
Impact and Implications: Security concerns directly impact consumer trust. A lack of trust can hinder the adoption rate of mobile payment systems.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between security and mobile payments is crucial. Addressing security concerns is paramount for fostering consumer confidence and driving the widespread adoption of mobile payment technology. Ongoing investment in advanced security measures is essential for the continued growth and success of this transformative technology.
Further Analysis: Examining Security Protocols in Greater Detail
A detailed examination of various security protocols reveals their critical role in protecting sensitive data within mobile payment systems. This involves analyzing the strengths and limitations of different encryption methods, authentication protocols, and fraud detection systems. Understanding these protocols is vital for stakeholders in the mobile payment ecosystem to ensure the security and integrity of transactions.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Mobile Payments
What is mobile payment? Mobile payment is a way to make purchases using a mobile device like a smartphone or tablet instead of physical cash or cards.
How secure are mobile payments? Mobile payment systems employ multiple layers of security, including encryption, tokenization, and biometric authentication to protect user data.
What are the different types of mobile payments? There are several types, including NFC, QR codes, mobile wallets, SMS-based payments, and in-app payments.
Are mobile payments accepted everywhere? The acceptance of mobile payments varies depending on location and merchant infrastructure.
What happens if my phone is lost or stolen? Most mobile payment systems allow you to remotely lock or disable your account to prevent unauthorized access.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Mobile Payments
-
Choose reputable apps: Download mobile payment apps from trusted sources.
-
Enable security features: Utilize biometric authentication and two-factor authentication where available.
-
Regularly review transactions: Monitor your transactions regularly to detect any unusual activity.
-
Keep software updated: Ensure your mobile operating system and payment apps are up to date with the latest security patches.
-
Be aware of phishing scams: Be cautious of suspicious emails or messages asking for personal information.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Mobile payments are revolutionizing the way we transact, offering unparalleled convenience and efficiency. While security concerns remain a key consideration, the ongoing development and improvement of security protocols ensure the continued growth and adoption of this transformative technology. As technology advances and consumer trust increases, mobile payments will continue to play a significant role in shaping the future of commerce.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Paying Off Student Loans Help Credit Score
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Does Paying Off Student Loans Affect Credit
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Long After Paying Off Student Loans Does It Affect Credit Score
Apr 07, 2025
-
Does Paying Off Student Loans Hurt Your Credit Score
Apr 07, 2025
-
Does Not Paying Back Student Loans Affect Credit Score
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Mobile Payment And How Does It Work . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.