What Is A Grace Period In Terms Of Credit Card Payments
adminse
Apr 02, 2025 · 9 min read
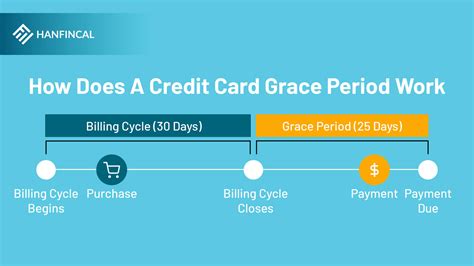
Table of Contents
Understanding the Grace Period: Navigating Your Credit Card Payments
What if missing a credit card payment's grace period could significantly impact your financial future? Understanding and effectively utilizing the grace period is crucial for maintaining a healthy credit score and avoiding unnecessary fees.
Editor’s Note: This article on credit card grace periods has been updated today to reflect current industry practices and provide the most up-to-date information for consumers.
Why the Grace Period Matters: Avoiding Interest Charges and Protecting Your Credit
The grace period on a credit card is a critical component of responsible credit card management. It's the period after your billing cycle ends and before your payment is due, during which you can pay your statement balance in full without incurring interest charges. This seemingly small window offers significant financial benefits, primarily preventing the accumulation of interest, which can quickly spiral into substantial debt. Beyond the financial implications, failing to utilize the grace period correctly can negatively affect your credit score, potentially making it harder to secure loans, rent an apartment, or even get a job in the future.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article will provide a comprehensive explanation of credit card grace periods, covering their definition, how they work, factors influencing their length, the consequences of missing the grace period, strategies for effective utilization, and frequently asked questions. Readers will gain a thorough understanding of this crucial aspect of credit card management and how to best leverage it to their advantage.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon information from leading financial institutions, consumer protection agencies, and reputable financial publications. Data on average grace periods, interest rates, and the impact of late payments on credit scores has been compiled to ensure accuracy and relevance. The information presented is intended to provide a clear, unbiased, and actionable guide for consumers.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition of Grace Period: A detailed explanation of what a grace period entails.
- How Grace Periods Work: A step-by-step illustration of the billing cycle and grace period.
- Factors Affecting Grace Period Length: Identification of variables influencing grace period duration.
- Consequences of Missing the Grace Period: A clear outline of the financial and credit penalties.
- Strategies for Effective Utilization: Practical tips and advice for maximizing grace periods.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Addressing common consumer inquiries.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a foundational understanding of the importance of the grace period, let's delve into the specifics of how it operates and the factors that influence its length.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Credit Card Grace Periods
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A grace period, in the context of credit card payments, is the time allotted between the end of your billing cycle and the due date for your payment. During this period, if you pay your statement balance in full, you avoid paying interest on the purchases made during the previous billing cycle. It's crucial to understand that this only applies to the statement balance—any new purchases made after the statement closing date will accrue interest from the transaction date, regardless of when you pay your statement balance.
2. How Grace Periods Work:
The process unfolds as follows:
- Billing Cycle: Your credit card company sets a billing cycle, typically a month. All purchases made within that cycle are tallied at the end.
- Statement Generation: At the end of the billing cycle, a statement is generated showing your purchases, payments, and the current balance.
- Grace Period Begins: The grace period starts the day after the statement closing date.
- Payment Due Date: The due date is usually clearly stated on your statement, typically 21-25 days after the statement closing date. This marks the end of your grace period.
- Payment in Full: Paying the full statement balance before the due date ensures you avoid interest charges. This balance does not include new purchases made after the statement closing date.
- Interest Accrual: If you only pay a portion of your statement balance or fail to pay by the due date, interest will be charged on the outstanding amount. This interest is calculated daily from the transaction date of the unpaid purchase.
3. Factors Affecting Grace Period Length:
While most credit cards offer a grace period of around 21-25 days, several factors can influence its length:
- Issuer Policies: Different credit card companies may have varying grace period lengths.
- Card Type: Some premium cards may offer longer grace periods as a perk.
- Payment History: Consistently paying your bills on time is likely to maintain your grace period, while consistently late payments might not negatively affect your grace period directly but could trigger penalties on the account in other ways.
- Account Terms and Conditions: Always carefully review your credit card agreement for the specific grace period terms that apply to your account.
4. Consequences of Missing the Grace Period:
Missing the grace period has several significant repercussions:
- Interest Charges: The most immediate consequence is incurring interest charges on your outstanding balance. This interest is calculated daily, compounding the debt.
- Late Payment Fees: Many credit card companies impose late payment fees, adding to the overall cost. These fees can range from $25 to $40 or more.
- Negative Impact on Credit Score: Late payments are reported to credit bureaus, leading to a drop in your credit score. A lower score can make it more difficult to secure loans, rent an apartment, or even get a job, as many employers perform credit checks.
- Account Suspension or Closure: In severe cases of persistent late payments, your credit card company may suspend or close your account.
5. Strategies for Effective Utilization:
Effectively using your grace period requires proactive planning and discipline:
- Understand Your Billing Cycle and Due Date: Familiarize yourself with your credit card statement and mark the payment due date on your calendar.
- Set Payment Reminders: Use online banking tools, calendar reminders, or mobile apps to ensure timely payments.
- Automate Payments: Consider setting up automatic payments to avoid forgetting due dates.
- Pay in Full: Always strive to pay your statement balance in full before the due date.
- Monitor Your Account Regularly: Keep track of your transactions and balances to avoid unexpected surprises.
Exploring the Connection Between Payment Habits and Grace Period Utilization
The relationship between consistent on-time payments and the effective use of the grace period is symbiotic. While consistently missing payments won’t directly shorten your grace period, it will lead to penalties and damage your credit score, undermining the benefits of the grace period. Let’s explore this connection further:
Key Factors to Consider:
Roles and Real-World Examples: A customer consistently paying late might find their credit limit reduced, increasing the likelihood of exceeding the credit limit and incurring further fees. This reduces the utility of the grace period as they're more likely to carry a balance. Conversely, a customer who consistently pays on time and in full benefits maximally from the grace period, avoiding interest charges entirely and building a strong credit history.
Risks and Mitigations: The primary risk is accumulating interest and late payment fees, leading to a cycle of debt. Mitigation involves proactive payment scheduling, utilizing online banking tools, and budgeting effectively to ensure sufficient funds are available before the payment due date.
Impact and Implications: The long-term impact of consistently missing payments and foregoing the grace period is a lower credit score, increased debt, and potential financial difficulties. Conversely, consistent on-time payments lead to improved credit scores, lower borrowing costs, and increased financial stability.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between responsible payment habits and grace period utilization is undeniable. By paying on time and in full, consumers not only avoid the negative consequences of missed payments but also maximize the advantages of the grace period, resulting in significant long-term financial benefits.
Further Analysis: Examining Interest Calculation in Greater Detail
Credit card interest is typically calculated using the average daily balance method. This means the interest is calculated based on the average balance you have on your card each day throughout the billing cycle. Understanding this calculation helps consumers grasp the importance of paying down their balances as quickly as possible to minimize interest charges. Factors such as the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and the balance carried forward also heavily influence the amount of interest you incur.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Grace Periods
What is a grace period? A grace period is the time between the end of your billing cycle and the due date for your payment, during which you can pay your statement balance in full without incurring interest.
How long is a grace period? Typically, grace periods range from 21 to 25 days, but this can vary depending on the credit card issuer and your account terms.
What happens if I miss my grace period? You will be charged interest on the outstanding balance and may also incur late payment fees. This will also negatively affect your credit score.
Can I still get a grace period if I make a partial payment? No, a grace period only applies if you pay your statement balance in full.
How can I avoid missing my grace period? Set up automatic payments, mark the due date on your calendar, or use online banking reminders.
What if my statement doesn't show a grace period? Check your credit card agreement for the terms and conditions, and contact the issuer if you still have questions.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of the Grace Period
- Set up automatic payments: This ensures timely payments and eliminates the risk of missing the due date.
- Monitor your account regularly: Track your spending and ensure you stay within your budget.
- Pay more than the minimum payment: Aim to pay the statement balance in full to avoid interest charges.
- Read your credit card statement carefully: Understand your billing cycle, due date, and interest rate.
- Explore budgeting tools: Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track spending and manage your finances.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
The credit card grace period is a valuable financial tool that, when used effectively, can significantly reduce the cost of credit. Understanding its mechanics, avoiding late payments, and employing effective management strategies will empower consumers to maximize its benefits and maintain healthy financial habits. By utilizing the insights provided in this article, readers can confidently navigate their credit card payments and prevent the unnecessary accumulation of debt and damage to their credit scores.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Bad Money Management
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is Poor Financial Management In Business
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is Poor Financial Management
Apr 06, 2025
-
Review Money Manager
Apr 06, 2025
-
Apps To Manage Money
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Grace Period In Terms Of Credit Card Payments . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.