What Is Fund Of Funds With Example
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 9 min read
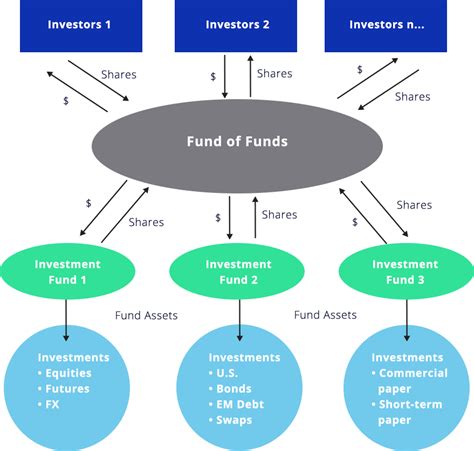
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Power of Fund of Funds: A Comprehensive Guide
What if accessing diverse investment strategies and expert portfolio management was simpler than you think? Fund of Funds (FoFs) offer a sophisticated yet accessible pathway to diversified investment portfolios, mitigating risk and maximizing potential returns.
Editor’s Note: This article on Fund of Funds (FoFs) provides a comprehensive overview of this investment vehicle, exploring its mechanics, benefits, risks, and practical applications. Updated information ensures readers have access to the latest insights in this dynamic investment landscape.
Why Fund of Funds Matter:
Fund of Funds, often abbreviated as FoFs, are investment vehicles that invest in a portfolio of other investment funds rather than directly in individual assets like stocks or bonds. Their importance lies in their ability to provide diversification, professional management, and access to specialized investment strategies that might be otherwise inaccessible to individual investors. FoFs are particularly relevant in today's complex financial markets, offering a way to navigate diverse asset classes and investment styles with relative ease. They are used by both institutional investors (like pension funds and endowments) and high-net-worth individuals seeking sophisticated portfolio construction.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will delve into the core aspects of Fund of Funds, exploring its definition, underlying mechanisms, advantages and disadvantages, regulatory considerations, and real-world examples. We will also examine specific types of FoFs and discuss how they fit into broader investment strategies. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of FoFs and their potential role in portfolio diversification and risk management.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This in-depth analysis incorporates insights gleaned from leading financial publications, regulatory documents, and expert interviews. Data-driven research has been meticulously incorporated to support claims and offer a balanced perspective on the merits and drawbacks of FoFs. The article strives to present accurate and readily understandable information for both seasoned investors and those new to the concept.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear explanation of FoFs and their fundamental principles.
- Types of Fund of Funds: Exploration of various FoFs, categorized by asset class, investment strategy, and target investor.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: A balanced assessment of the benefits and risks associated with FoF investments.
- Regulatory Landscape: An overview of the regulatory environment governing FoFs.
- Real-World Examples: Case studies illustrating successful and unsuccessful FoF implementations.
- Selecting a Fund of Funds: Practical advice and criteria for choosing the right FoF based on individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the significance of Fund of Funds, let's now dissect their key aspects, offering a detailed exploration of their composition, functioning, and implications for investors.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Fund of Funds:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A Fund of Funds is an investment fund that invests in a portfolio of other investment funds, rather than directly in individual stocks, bonds, or other assets. Think of it as a "fund of funds" – a fund that invests in a collection of other funds managed by different investment managers. This indirect investment approach offers several advantages, such as diversification across various asset classes and investment strategies, and access to specialized expertise that individual investors might lack. The FoF manager selects underlying funds based on specific investment objectives, risk tolerance, and market outlook. The performance of the FoF is therefore a function of the performance of its underlying funds, weighted by their respective allocations within the FoF's portfolio.
2. Types of Fund of Funds:
FoFs are not a monolithic entity; they come in various forms, categorized based on several criteria:
-
By Asset Class: FoFs can focus on specific asset classes, such as equity FoFs (investing in stock funds), fixed-income FoFs (investing in bond funds), real estate FoFs (investing in real estate funds), or multi-asset FoFs (investing across various asset classes).
-
By Investment Strategy: FoFs can follow different investment strategies, such as growth-oriented FoFs, income-oriented FoFs, or value-oriented FoFs. Some FoFs might employ a more active management style, while others might adopt a passive, index-tracking approach.
-
By Target Investor: FoFs are designed for different investor profiles. Some cater to retail investors, while others target institutional investors with higher investment minimums and more sophisticated investment objectives. Hedge fund FoFs, for instance, are typically accessible only to accredited investors due to the higher risk and complexity of hedge fund investments.
3. Advantages of Fund of Funds:
- Diversification: FoFs provide instant diversification across multiple asset classes, investment strategies, and geographies, mitigating risk.
- Professional Management: FoFs are managed by experienced professionals who select and monitor underlying funds, relieving investors of the burden of individual fund selection and management.
- Access to Expertise: FoFs provide access to specialized expertise and investment strategies that may be beyond the reach of individual investors.
- Simplicity: FoFs simplify the investment process by consolidating multiple investments into a single vehicle.
- Reduced Transaction Costs: While FoFs incur fees, they can sometimes reduce overall transaction costs compared to directly investing in multiple individual funds.
4. Disadvantages of Fund of Funds:
- Higher Fees: FoFs charge management fees on top of the fees charged by the underlying funds, leading to potentially higher overall costs. These fees can significantly impact the net return.
- Lack of Transparency: Understanding the precise composition and performance of all underlying funds can be challenging due to layers of indirect investment.
- Potential for Misalignment of Interests: Conflicts of interest may arise between the FoF manager and the managers of underlying funds.
- Performance Dependence: The performance of an FoF is directly tied to the performance of its underlying funds. Poor performance in one or more underlying funds can negatively impact the FoF's overall returns.
- Liquidity Risk: The liquidity of an FoF is dependent on the liquidity of its underlying funds. Redeeming investments from an illiquid FoF might be challenging.
5. Regulatory Landscape:
The regulatory environment for FoFs varies depending on the jurisdiction and the types of underlying funds. Regulations typically cover areas such as investor protection, disclosure requirements, and fund governance. Compliance with relevant regulations is crucial for FoF managers to operate legally and ethically. In many jurisdictions, FoFs are subject to similar regulatory scrutiny as other collective investment schemes.
6. Real-World Examples:
Numerous examples of FoFs exist across various asset classes and investment strategies. Some prominent examples include FoFs that invest in private equity, real estate, or hedge funds. The success of an FoF is contingent on the selection of high-performing underlying funds and the skill of the FoF manager in managing the overall portfolio. Analyzing historical performance data of FoFs is crucial in understanding their track record and potential risks.
Exploring the Connection Between Due Diligence and Fund of Funds:
The relationship between thorough due diligence and the success of a Fund of Funds is paramount. Effective due diligence plays a crucial role in mitigating risks and maximizing returns.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Due diligence involves scrutinizing the track records, investment strategies, and management teams of the underlying funds. Analyzing past performance data and conducting thorough background checks on fund managers are crucial steps. For example, an FoF investing in emerging market equities would require extensive due diligence on the political and economic stability of the target countries.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Risks associated with FoFs include poor performance of underlying funds, high fees, and lack of transparency. Mitigating these risks requires careful fund selection, diversification across various asset classes and strategies, and continuous monitoring of the FoF's performance.
-
Impact and Implications: The impact of effective due diligence is significant. It can enhance the chances of selecting high-performing underlying funds, leading to improved risk-adjusted returns for the FoF and its investors. Conversely, inadequate due diligence can expose the FoF to considerable risks.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The interplay between robust due diligence and successful Fund of Funds management is undeniable. By rigorously assessing the underlying funds and employing proactive risk management strategies, FoFs can effectively navigate market fluctuations and achieve their investment objectives.
Further Analysis: Examining Due Diligence in Greater Detail:
The depth of due diligence required for an FoF varies based on the complexity of the underlying funds and the investment strategy employed. For instance, due diligence on an FoF investing in hedge funds requires a significantly higher level of scrutiny than that for an FoF investing in established index funds. This in-depth examination encompasses analyzing financial statements, conducting independent valuations, and assessing the management team's experience and expertise.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Fund of Funds:
-
What is a Fund of Funds? A Fund of Funds (FoF) is an investment vehicle that invests in a portfolio of other investment funds rather than directly in individual securities.
-
How do Fund of Funds work? FoFs pool investor capital to invest in a diversified selection of underlying funds, aiming to achieve specific investment objectives. The FoF manager selects and monitors these underlying funds, often employing specialized knowledge to achieve portfolio diversification and enhanced returns.
-
What are the advantages of investing in Fund of Funds? Advantages include diversification, professional management, access to specialized expertise, and simplified investment process.
-
What are the risks associated with Fund of Funds? Risks include higher fees compared to direct investments, potential lack of transparency, performance dependence on underlying funds, and liquidity risk.
-
How can I choose a Fund of Funds? Carefully research the FoF's investment strategy, fees, track record, and the experience of its management team. Consider your investment goals and risk tolerance when making your selection.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Fund of Funds:
-
Understand Your Investment Goals: Clearly define your investment objectives (e.g., capital appreciation, income generation) before selecting an FoF.
-
Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Carefully evaluate the FoF's investment strategy, fees, historical performance, and management team.
-
Diversify Your Portfolio: Don't over-concentrate your investments in a single FoF. Diversify across different FoFs and other asset classes to reduce risk.
-
Monitor Your Investments: Regularly review the performance of your FoF and make adjustments as needed.
-
Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a qualified financial advisor to determine if an FoF is suitable for your investment needs.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Fund of Funds offer a compelling pathway to diversified investment portfolios and access to specialized expertise. However, it is imperative to conduct thorough due diligence, understand the associated risks, and align the FoF's investment strategy with your individual goals and risk tolerance. By carefully considering these factors, investors can leverage the potential benefits of FoFs while mitigating their inherent risks. Remember, investing in any fund involves risk, and the value of investments can fluctuate. It is essential to conduct thorough research and seek professional financial advice before making any investment decisions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Pass Optus Credit Check
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass Telstra Credit Check
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass Credit Check For Phone
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass Credit Check For Mobile Phones Samsung
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass Credit Check For Car Finance
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Fund Of Funds With Example . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.