What Is Bank Frauds Examples
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 8 min read
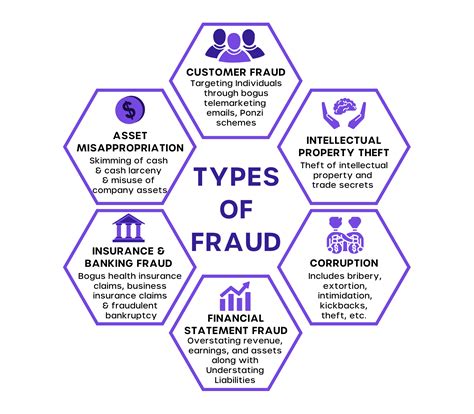
Table of Contents
Unmasking Bank Fraud: Types, Examples, and Prevention
What if the seemingly impenetrable fortress of modern banking is vulnerable to sophisticated and devastating attacks? Bank fraud, a pervasive threat, represents a significant risk to individuals, businesses, and the global financial system.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive article on bank fraud provides up-to-date insights into various types, real-world examples, and effective prevention strategies. Readers will gain a deeper understanding of the evolving landscape of financial crime and the measures needed to safeguard against it.
Why Bank Fraud Matters:
Bank fraud encompasses a wide range of illicit activities aimed at illegally obtaining money or other assets from financial institutions. Its impact extends beyond monetary losses; it erodes public trust, disrupts economic stability, and can lead to significant reputational damage for banks and individuals alike. The increasing reliance on digital banking channels has further amplified the vulnerability to sophisticated cyber-attacks, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced security measures and fraud detection systems. The ramifications of successful bank fraud extend to increased transaction costs, stricter regulations, and potentially higher interest rates for consumers.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article delves into the multifaceted world of bank fraud, exploring various types, providing illustrative examples, and examining preventative measures. We will explore common techniques like check fraud, wire fraud, and phishing scams, while also examining the increasingly prevalent issue of cyber-fraud and insider threats. The discussion will include real-world cases, highlighting the impact and consequences of such criminal activities. Finally, we will outline strategies for mitigating risk and fostering a more secure banking environment.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article draws upon extensive research from reputable sources, including official reports from financial regulatory bodies, academic publications, news articles detailing high-profile cases, and insights from cybersecurity experts. The information presented is meticulously fact-checked to ensure accuracy and provide readers with a reliable and informed perspective on bank fraud.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A comprehensive definition of bank fraud and its various categories.
- Types of Bank Fraud: Detailed explanations of common fraud schemes, including check fraud, credit card fraud, wire fraud, loan fraud, identity theft, and cyber-fraud.
- Real-World Examples: Case studies illustrating the methods employed by fraudsters and the resulting consequences.
- Prevention Strategies: Practical steps individuals and banks can take to mitigate the risk of fraud.
- The Role of Technology: The impact of technology on both perpetrating and preventing bank fraud.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the significance of understanding bank fraud, let's now explore its various forms and the methods employed by perpetrators.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Bank Fraud:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Bank fraud broadly refers to any illegal activity designed to deceive or defraud a bank or its customers. This encompasses a wide range of actions, from forging signatures on checks to sophisticated cyberattacks targeting online banking systems. The common thread is the intention to illegally obtain funds, assets, or services.
2. Types of Bank Fraud:
-
Check Fraud: This involves forging checks, altering existing checks, or using stolen checks to obtain funds. Techniques range from simple counterfeiting to more advanced methods involving altering check numbers or account details.
-
Credit Card Fraud: This includes unauthorized use of credit cards, either through stolen cards, card cloning, or phishing scams that obtain card details. Online transactions are particularly vulnerable.
-
Wire Fraud: This type of fraud involves manipulating wire transfers to redirect funds to unauthorized accounts. This often targets businesses with large transactions, exploiting vulnerabilities in internal controls.
-
Loan Fraud: This involves misrepresenting information on loan applications to obtain loans that would otherwise be denied. This can involve falsifying income, assets, or credit history.
-
Identity Theft: Fraudsters steal personal information, including Social Security numbers, addresses, and bank account details, to open fraudulent accounts or make unauthorized transactions.
-
Cyber Fraud: This increasingly prevalent form of bank fraud utilizes technology to target online banking systems. Phishing emails, malware, and ransomware attacks are common methods used to gain access to accounts and steal funds. This also includes sophisticated attacks targeting bank servers directly.
-
Insider Fraud: This involves employees of the bank colluding with external parties or acting alone to defraud the institution. This can range from manipulating transactions to stealing customer information.
3. Real-World Examples:
-
The Equity Funding Scandal (1970s): This involved a massive accounting fraud where Equity Funding Corporation of America inflated its assets by creating fictitious insurance policies, resulting in billions of dollars in losses.
-
The Madoff Ponzi Scheme (2008): Bernie Madoff's scheme defrauded thousands of investors by paying returns to earlier investors with money from newer investors, ultimately collapsing and causing billions in losses. While not directly targeting a bank, it highlights the vulnerability of the financial system to large-scale fraud.
-
The 2016 Bangladesh Bank Heist: Hackers stole $81 million from the Bangladesh central bank's account at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York by exploiting vulnerabilities in the SWIFT international payment system.
-
Numerous phishing and smishing attacks: Everyday individuals are targeted by emails or text messages designed to appear legitimate, requesting account details or login credentials. Successful phishing attacks can lead to immediate account compromise and significant financial losses.
4. Prevention Strategies:
-
Strong Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication, requiring more than just a password to access accounts.
-
Employee Training: Educating employees about fraud awareness and best security practices, including recognizing phishing emails and reporting suspicious activity.
-
Fraud Detection Systems: Utilizing advanced technologies to monitor transactions for unusual patterns and flag potentially fraudulent activity.
-
Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary safeguards.
-
Customer Education: Educating customers about the signs of fraud, best practices for protecting their financial information, and reporting suspicious activity promptly.
-
Data Encryption: Protecting sensitive customer data with strong encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Regular Software Updates: Keeping all software and systems up-to-date to patch security vulnerabilities.
5. The Role of Technology:
Technology plays a dual role in bank fraud: it facilitates fraudulent activities, but also offers powerful tools to detect and prevent them. While sophisticated cyberattacks pose significant threats, advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms are being increasingly deployed to identify suspicious patterns and proactively mitigate risks. Blockchain technology is also explored as a potential solution for enhancing transparency and security in financial transactions.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
Bank fraud is a persistent and evolving threat to the global financial system. Its diverse forms and sophisticated techniques require a multi-layered approach to prevention, incorporating technological advancements, rigorous security measures, and robust employee training. A proactive and collaborative effort between banks, regulators, and customers is crucial in mitigating the risk and protecting the integrity of the financial system.
Exploring the Connection Between Cybersecurity and Bank Fraud:
Cybersecurity is inextricably linked to bank fraud. Many modern fraud schemes rely heavily on exploiting vulnerabilities in online systems and networks. The rapid growth of digital banking and online transactions has made financial institutions a prime target for cybercriminals.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Cyberattacks, ranging from phishing scams to sophisticated malware infections targeting bank servers, demonstrate the critical role cybersecurity plays in preventing fraud. The 2016 Bangladesh Bank heist exemplifies the devastating impact of successful cyberattacks on financial institutions.
-
Risks and Mitigations: The risks associated with inadequate cybersecurity measures include data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Mitigations involve implementing robust security protocols, regularly updating software, employing firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and providing cybersecurity training to employees.
-
Impact and Implications: Weak cybersecurity practices not only expose banks to direct financial losses but also damage customer trust and may lead to regulatory penalties and increased insurance premiums. Strong cybersecurity measures are essential to maintaining public confidence and preserving the stability of the financial system.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The connection between cybersecurity and bank fraud is undeniable. Strengthening cybersecurity infrastructure is not merely a technological imperative; it's fundamental to safeguarding the financial system and preventing significant economic losses. A robust cybersecurity strategy is a crucial component of any effective bank fraud prevention plan.
Further Analysis: Examining Cybersecurity in Greater Detail:
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. Banks must stay ahead of the curve by investing in advanced security technologies, regularly updating their systems, and providing ongoing training to their employees. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in fraud detection is becoming increasingly vital in identifying and preventing sophisticated attacks.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Bank Fraud:
-
What is the most common type of bank fraud? Check fraud and credit card fraud remain prevalent, but cyber-fraud is rapidly gaining ground.
-
How can I protect myself from bank fraud? Be vigilant about phishing emails, use strong passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and regularly monitor your bank accounts for unusual activity.
-
What should I do if I suspect I've been a victim of bank fraud? Immediately contact your bank and report the fraudulent activity to the appropriate authorities.
-
What role do banks play in preventing bank fraud? Banks are responsible for implementing robust security measures, training their employees, and investing in fraud detection technologies.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Fraud Prevention:
-
Regularly review your bank statements: Look for any unauthorized transactions or unusual activity.
-
Use strong and unique passwords: Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
-
Be cautious of phishing emails: Don't click on links or open attachments from unknown senders.
-
Shred sensitive documents: Properly dispose of documents containing personal financial information.
-
Monitor your credit report: Regularly check for any fraudulent accounts or inquiries.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Bank fraud represents a significant and evolving threat to individuals and financial institutions alike. Understanding the different types of fraud, recognizing the signs, and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial steps in safeguarding against this pervasive crime. A collective effort involving banks, regulators, and individuals is essential to maintaining a secure and trustworthy financial system. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, we can collectively work towards a future where bank fraud is significantly minimized.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Pass Credit Check For Car Finance
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass Credit Check For Mobile Phones
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass A Rental Credit Check For Free
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass A Credit Score Check
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass A Rental Credit Check Reddit
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Bank Frauds Examples . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.