What Does A Grace Period Mean In Finance
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 8 min read
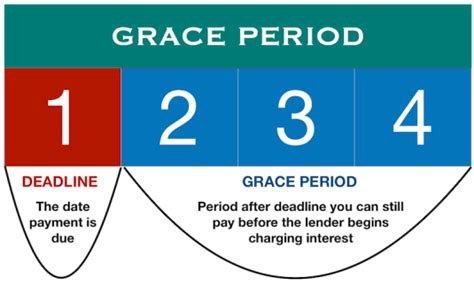
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Grace Period: A Comprehensive Guide to Financial Flexibility
What if navigating financial obligations was simpler, offering a cushion against unforeseen circumstances? Grace periods, often overlooked yet incredibly valuable, provide precisely that—a buffer zone within the financial landscape.
Editor’s Note: This article on grace periods in finance was published today, offering readers up-to-date insights into this crucial aspect of financial management. Understanding grace periods can significantly improve your financial planning and reduce stress related to missed payments.
Why Grace Periods Matter: Avoiding Late Fees and Maintaining Creditworthiness
Grace periods are essentially short-term extensions offered by lenders or service providers, allowing individuals or businesses to delay a payment without immediately incurring penalties. Their importance stems from their ability to prevent late payment fees, maintain a positive credit history, and offer a crucial buffer during unexpected financial difficulties. Grace periods are relevant across a wide spectrum of financial products, including credit cards, loans, insurance premiums, and subscriptions. Understanding their nuances is paramount for responsible financial management. This understanding empowers individuals to make informed decisions and avoid potentially damaging consequences.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article delves into the multifaceted world of grace periods in finance. We'll explore their definitions across different financial products, outline their durations and conditions, examine the implications of failing to utilize them effectively, and offer practical advice for managing financial obligations proactively. The discussion will also highlight the importance of understanding the specific terms and conditions associated with each grace period, emphasizing the need for careful reading of contracts and agreements.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the product of extensive research, drawing upon authoritative financial sources, industry best practices, and legal definitions related to grace periods. Information is cross-referenced and verified to ensure accuracy and reliability, providing readers with a trustworthy and comprehensive understanding of the subject. The goal is to empower readers with the knowledge they need to navigate financial situations confidently and responsibly.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A precise definition of grace periods and their fundamental principles.
- Applications Across Industries: How grace periods are applied across various financial sectors.
- Challenges and Solutions: Potential pitfalls related to grace periods and strategies for mitigation.
- Impact on Financial Well-being: The overall effect of grace periods on personal and business finances.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the significance of grace periods, let's delve into the specifics, exploring their application across diverse financial instruments and the critical factors influencing their implementation.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Grace Periods
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A grace period, in finance, is a designated timeframe after a payment's due date during which a payment can be made without incurring late fees or penalties. The duration of this period varies considerably depending on the type of financial agreement and the specific lender or provider. This period provides crucial breathing room, allowing individuals to address temporary financial setbacks without immediately facing negative repercussions. It's vital to remember that a grace period is not a forgiveness of debt; it is simply a postponement of the payment due date.
2. Applications Across Industries:
-
Credit Cards: Most credit cards offer a grace period, typically 21-25 days, after the billing cycle closes. During this period, if you pay your statement balance in full, you won't incur interest charges. However, if you only make a partial payment, interest will accrue on the outstanding balance from the transaction date.
-
Loans: Loan grace periods are less common than credit card grace periods and usually apply to specific loan types, such as student loans or certain types of business loans. These periods often defer payments for a set duration, usually a few months, before regular payments commence. The terms and conditions are strictly defined in the loan agreement.
-
Insurance Premiums: Insurance policies often include a grace period, usually 30 days, after the due date of a premium payment. While the policy remains active during this period, late payment fees may still apply. Failure to pay within the grace period may lead to policy cancellation.
-
Subscriptions: Subscription services, like streaming platforms or software licenses, frequently have grace periods, often ranging from a few days to several weeks. These periods allow subscribers to rectify missed payments without immediate service interruption.
3. Challenges and Solutions:
-
Misunderstanding Grace Period Terms: Many individuals misunderstand the precise terms and conditions associated with grace periods. This can lead to unexpected late fees or penalties. Carefully reading the fine print of all financial agreements is crucial to avoid such situations.
-
Over-Reliance on Grace Periods: While grace periods provide a safety net, consistently relying on them to manage finances is not sustainable. It's essential to develop responsible budgeting and payment strategies to avoid recurring late payments.
-
Missed Grace Periods: Failing to make payments within the grace period results in late fees, negatively impacting credit scores and potentially leading to further financial complications.
Solutions:
-
Set Reminders: Utilize calendar reminders, automated payment systems, or mobile banking apps to ensure timely payments.
-
Budget Effectively: Create a realistic budget that accounts for all financial obligations, leaving a buffer for unforeseen expenses.
-
Communicate with Lenders: If facing financial difficulties, contact lenders immediately to discuss potential repayment options. Many lenders are willing to work with borrowers facing temporary hardships.
4. Impact on Financial Well-being:
Grace periods have a profound impact on individual and business financial health. They prevent the snowball effect of accumulating late fees and protect credit scores. Maintaining a good credit rating is crucial for accessing favorable interest rates on loans, mortgages, and other financial products. By preventing late payments, grace periods contribute to long-term financial stability and peace of mind.
Exploring the Connection Between Credit Scores and Grace Periods
The relationship between credit scores and grace periods is significant. While successfully utilizing a grace period doesn't directly boost your credit score, failing to do so can severely damage it. Late payments, a direct consequence of missing a grace period, are a major factor negatively impacting credit scores. Lenders and credit bureaus view late payments as indicators of poor financial responsibility, leading to lower credit scores, which, in turn, can make it more difficult to obtain loans or secure favorable interest rates in the future.
Key Factors to Consider:
Roles and Real-World Examples: A missed credit card payment within the grace period can lead to a late payment fee, a damaged credit score, and potentially higher interest rates on future loans. Similarly, missing an insurance premium payment during the grace period could result in policy cancellation, leaving one vulnerable to unforeseen risks.
Risks and Mitigations: The primary risk associated with grace periods is the potential for misunderstanding their terms and conditions, leading to late payments. Mitigation strategies include setting payment reminders, carefully reviewing financial agreements, and actively managing personal finances.
Impact and Implications: The impact of utilizing or missing grace periods extends far beyond immediate financial consequences. Consistent successful use fosters positive financial habits, while missed grace periods can trigger a downward spiral of late payments, debt accumulation, and damaged creditworthiness.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The connection between diligent management of grace periods and overall financial well-being is undeniable. By understanding the nuances of grace periods and acting proactively, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce the risk of late payments, protect their credit scores, and maintain a stable financial footing.
Further Analysis: Examining Credit Repair Strategies in Relation to Grace Periods
Even after a grace period has been missed, and a late payment has negatively impacted a credit score, there are steps that can be taken to repair credit. These strategies include consistently making on-time payments moving forward, paying down outstanding debt, and possibly working with a credit counseling agency. While rebuilding credit takes time and effort, it is possible to recover from a negative impact caused by a missed grace period.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Grace Periods
Q: What happens if I miss a grace period? A: Missing a grace period usually results in late fees, penalties, and potentially negative impacts on credit scores. The specific consequences vary depending on the financial agreement.
Q: Are grace periods legally mandated? A: Grace periods are not universally mandated by law; rather, they are offered at the discretion of lenders and service providers, often detailed in the terms and conditions of the agreement.
Q: Can I negotiate an extension beyond the grace period? A: In some cases, it may be possible to negotiate an extension with the lender or service provider, but this is not guaranteed and depends on the lender's policies and your individual circumstances.
Q: How long are grace periods typically? A: The duration of grace periods varies depending on the financial product. Credit cards commonly offer 21-25 days, while insurance policies often provide a 30-day grace period.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Grace Periods
-
Read the Fine Print: Carefully review the terms and conditions of every financial agreement to understand the specifics of the grace period.
-
Utilize Automated Payments: Set up automated payments to avoid accidentally missing due dates.
-
Maintain a Financial Calendar: Use a calendar or budgeting app to track due dates and payment deadlines.
-
Communicate Proactively: If facing financial challenges, reach out to your lender or service provider to discuss potential solutions before missing a payment.
-
Build an Emergency Fund: Having an emergency fund can provide a safety net for unexpected expenses, reducing reliance on grace periods.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Grace periods are an often-underappreciated yet crucial aspect of personal and business finance. Understanding their mechanisms and utilizing them effectively can significantly contribute to financial stability and a positive credit history. By proactively managing finances and adhering to payment deadlines, individuals and businesses can avoid the pitfalls of missed grace periods and maintain a strong financial foundation. The responsible management of grace periods is a cornerstone of sound financial practices.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Speedy Cash Late Payment Fee
Apr 02, 2025
-
Speedy Cash Late Fee
Apr 02, 2025
-
Late Payment Chase Sapphire
Apr 02, 2025
-
Late Fee On Chase Credit Card
Apr 02, 2025
-
Will Chase Sapphire Waive Annual Fee
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does A Grace Period Mean In Finance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.